Performance Improvement Cycle
The performance improvement cycle is a component of the performance management cycle. The performance management cycle depicts all the stages involved in the process of planning, monitoring, reviewing, and rewarding performance. The performance improvement cycle focuses just on the improvement process.
About the Performance Improvement Cycle
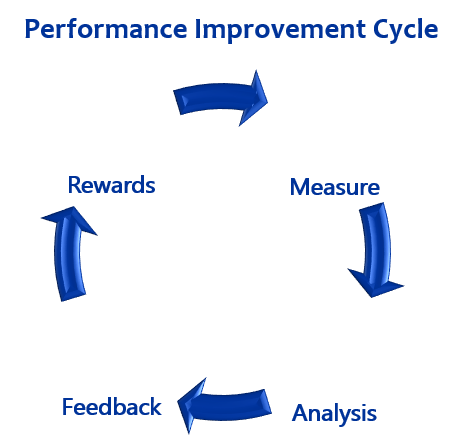
The performance improvement cycle begins with measuring the current performance levels. After you obtain the performance data, it needs to be analyzed to determine what went well and what needs improvement. After the analysis, you need to let the performer know what areas of their performance needs to improve. In order to help ensure the performance will improve, you need to recognize and reward the improved performance.
Four Components of the Performance Improvement Cycle
The Performance Improvement Cycle has for stages. Each one feeds into the next and continues to loop around.
- Measuring Performance
- Analyzing Performance
- Providing Feedback
- Recognizing and Rewarding
Measuring Performance
The first phase of the performance improvement cycle is performance measurement.
Performance measurement is the process of monitoring, collecting and reporting information regarding the performance of an individual or group in order to quantify the efficiency and effectiveness of their actions. What actually is measured will depend on what is important about that particular performance. Always focus on the important elements that are necessary to reach the goals and objective that have been set.
Analyzing Performance
After the data has been collected during the measuring stage, the next stage is performance analysis.
Performance analysis is the process of reviewing, evaluating, and interpreting data collected regarding an individual’s or group’s performance to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. This is when you assess the progress made towards achieving the predetermined performance goals. You will make comparisons of the actual performance to what was planned to be achieved. You would determine what caused any shortcomings and what could be done to improve performance.
Providing Feedback
After the data has been analyzed, it is time to provide feedback on the performance.
Feedback should be given in a thoughtful and positive manner, so the individual does not feel criticized. If the person receiving the feedback feels they are being criticized, they may become demotivated, perform slower, and/or become distracted. Basically, poor feedback can be worse than no feedback. Therefore, it important to give feedback that encourages the individual to take the information and use it to improve performance.
Additionally, the feedback should provide information, not judgments. Therefore, when giving feedback, focus on observable behavior instead of making broad judgments or giving personal opinions. Lastly, the feedback must make sense to the person so they can incorporate it into future performance.
Recognizing and Rewarding Performance
The final phase of the performance improvement cycle is recognizing and rewarding good performance. When a person gets rewarded for good performance, they will be more motivated to continue performing well. On the contrary, if quality performance is not recognized and rewarded it often with not be maintained.
Offering recognition and rewards for good performance will boost motivation to help ensure individuals stay on track and maintain a positive attitude. Recognition sends people a strong message that what they are doing matters. It makes them feel seen, heard, and valued. People who feel appreciated are more engaged and invested in their performance.