Chunking Information
Chunking refers to an approach for making more efficient use of short-term memory by grouping information. Chunking breaks up long strings of information into units or chunks. The resulting chunks are easier to commit to memory than a longer uninterrupted string of information.
Good chunking facilitates comprehension and retrieval of information.
Chunking Strategy
Chunking is a strategy used to reduce the cognitive load as the learner processes information. The learner groups content into small manageable units making the information easier to process. Essentially, chunking helps in the learning process by breaking long strings of information into bit size chunks that are easier to remember.
Chunking Process
There are several steps to the chunking process. The number of steps you use will depend on the type information you are chunking.
- Break larger amounts of information into smaller units
- Identify similarities or patterns
- Organize the information
- Group information into manageable units
Chunking Information
Chunking is used most commonly to organize or classify large amounts of information, even when there are no obvious patterns. Occurrences of chunking as a memory device can be seen in the way information is grouped in our daily life.
Simple Chunking
The breaking down of seemingly random numbers into chunks makes the number easier to remember.
Examples:
- Phone numbers are not typically seen or remembered as a long string of numbers like 8605554589, but rather 860-555-4589.
- Birthdates are typically not recalled by 11261995, but rather 11/26/1995.
Letters can also be broken down into chunks helping to remember easier.
Example:
“XLETHIPSOXWHYMIX” is difficult to remember as a long string of letters, however if the letters are grouped or chunked, remembering them is easier. The breaking down of the letters into more “logical” chunks also makes it easier to remember.
X LET HIP SOX WHY MIX
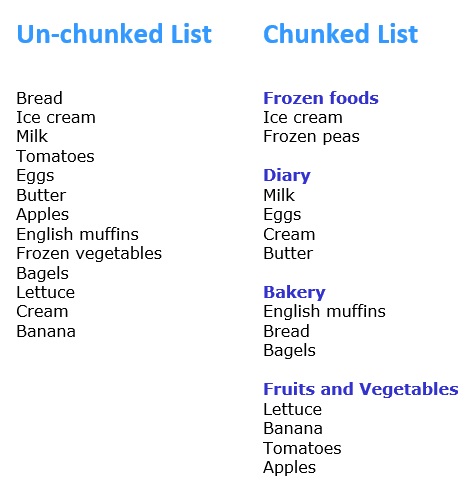
Chunking Lists
Chunking can also work for lists. For example, a shopping list can be segmented into categories.
Chunking Processes
Chunking can also work for processes. For example, painting a room may be divided into three groups;
- Preparation
- Painting
- Clean-up
Related Links