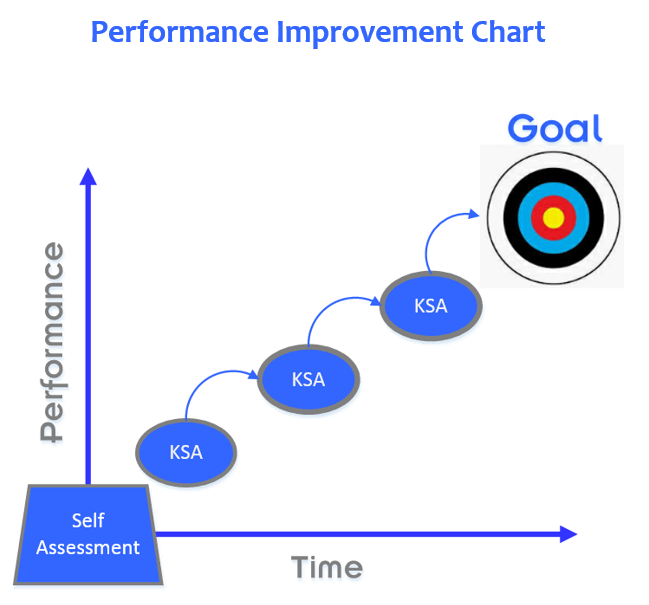
If you are looking to improve your performance, you need to take some basic steps. No matter if is in school, sports, business or life, the steps are the same. It starts with determining the performance gap, then identifying the knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSAs) that are needed to close that gap. After the KSAs are identified, set goals and implement an action plan to achieve those goals. The next step is to put that plan into action by developing the KSAs and periodically assessing your performance and make adjustments to close the performance gap.
Steps for the Performance Improvement Process
The performance improvement process:
- Determine the Performance Gap and its Causes
- Identify Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes (KSA) to Improve
- Set Performance Goals in an Action Plan
- Develop the Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes (KSA)
- Review Performance and Assess Progress Periodically
KSA and the Performance Improvement Process
Determine the Performance Gap and its Causes
The first step is to determine the performance gap of where you are and where you need to be. This is accomplished by identifying and defining what the expectations are in terms of your tasks, outcomes, and behaviors. After which, you assess your own performance level. You then determine the cause for the gap in performance.
Identify Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes (KSA) to Improve
Now that you know where you are and where you need to be, the second step is to identify what knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSAs) you will need in order to get to the desired level.
Knowledge: cognitive or mental abilities used to retain and process information
Skills: physical abilities used to perform activities or tasks
Attitudes: feelings or emotional about someone or something
To do this, you have to complete a self-assessment. A self-assessment is intended to find out what knowledge and skills you currently possess, and what knowledge and skills you will need to obtain and develop in order to reach your goals.
KSAs are an essential part of the performance improvement process. As your skills and knowledge increases, so does your ability to do.
Set Performance Goals in an Action Plan
The next step is to implement an action plan to close the gap and resolve the issues.
You start the action plan with the end in mind – what you want to ultimately accomplish. Therefore, set goals that will help you move towards improvement. These goals should be performance goals meaning they should be focused on your performance and not the outcome. This will give you much more control over the ability to achieve that goal.
Additionally, the goals should be specific, realistic, and measurable. Many people set SMART goals which stands for:
S – Specific
M – Measurable
A – Achievable
R – Relevant
T – Time-bound
This basic criterion can help structure your goals so they are easier to achieve.
Develop the Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes (KSA)
The fourth step is to develop the knowledge, skills and attitudes that you identified as needed to reach your goals. This can be accomplished through educational and training activities. With these activities you can acquire new knowledge, develop new skills, or form a new attitude.
Typically, most training and educational programs have focused on the development of knowledge and skills, as those are the ones that are most observable and easiest to measure. Attitudes, on the other hand, are addressed the least by traditional training and educational programs because they are the most difficult for people to develop, and are the hardest to measure for results.
Review Performance and Reassess Progress Periodically
The final step is continuous process of assesses your performance and making adjustments to close the gap. Periodically, set up performance assessments to check your progress towards your goals. Analyze the data and information you have collected from the performance assessment and compare it with the performance expectations. Make adjusts as needed to ensure you will reach your goals.