Course Design
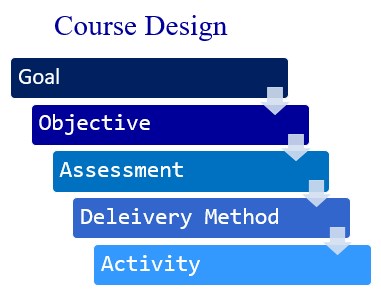
Course design includes the following tasks:
- Identify competencies
- Define learning goals
- Determine learning objectives
- Create assessments
- Develop instructional methods and strategies
- Develop activities
Elements of Course Design
Competencies – Arrays of the essential knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) required to achieve an acceptable level of performance.
Learning or Course Goal – Overall intended results or competencies for the learners to attain from the educational session.
Learning Objectives – Statements specifically describing what the learner will be able to do as a result of the course activities.
Assessments – Evidence to show the learner has met the objectives.
Delivery Methods and Strategies – Ways of communicating or imparting the new information to the learner.
Activities – Experiences that allow the learner to practice applying the new skills and knowledge.
Start With the End in Mind
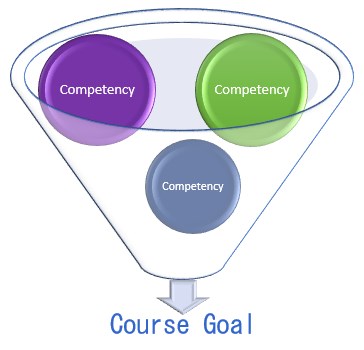
When designing a course, start with the end in mind. Training courses are designed by working backwards from desired competencies to method of instruction and activities. Therefore, you must first determine what competencies are needed to perform the necessary job functions and tasks.
Competencies are arrays of the essential knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) required to achieve an acceptable level of performance. Therefore, when determining competencies for a course, conduct a need analysis to determine the desired knowledge and abilities needed to perform the job tasks.
Learning or Course Goal
Once the desired competencies are identified, a learning goal should be defined. A learning goal is a general statement that describes the intended competency and desired knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) a participant needs to successfully perform after an educational session. The course goal is the overall expectation for what the participants will learn in a course.
The competencies are about what the individual will need to be able to do after the course to perform his or her job functions, while the learning goal is what the individual should learn in the course. The goal is a summary of the competencies. It provides direction and a point of reference for the course instruction. All course instructions, activities, and assessments should be aligned to ensure and effective learning course.
Alignment for Course Design
Course alignment is essential for an effective learning course. Alignment refers to the connection between course goals, objectives, instruction, activities, and assessments. If a course is properly aligned, it means the goals and objectives are directly related to the instruction, activities, and assessments. This alignment helps ensure that what is taught and practiced in the course will allow the learner to perform the necessary job functions.
Creating Learning Objectives
To ensure proper alignment, after the learning goal is defined, the next step is to determine learning objectives. Objectives are established by breaking those larger goals into smaller manageable pieces. This is done by unbundling the desired competencies into their basic parts to determine what the participant would need to know to perform this competency at a specific level. Hence, learning objectives are directly related to the competencies. These objectives are the measurable indicators of what the learner is expected to demonstrate upon completion of the course.
The main distinction between objectives and goals is that an objective is written so that it can be measured or assessed.
Assessments
Once learning objectives are established, the next step is to create assessments to confirm the learners have accomplished the learning objectives. Continuing with the theme of starting with the end in mind, create the assessments before you determine the instructional method or create the activities. This is because the assessments are at the end of the session and used as confirmation that learning took place.
Assessments are a mechanisms for collecting evidence that the learners have met the learning objectives. It is basically a test to verify and measure the degree to which the learner is able to apply what they have learned in the session. It helps to confirm that the course has met it intended goal.
Instructional Methods and Strategies
The next step is to determine the most effective ways to teach based on the assessments.
Instructional methods and strategies are the ways of communicating and imparting the new information to the learner. In order to make learning effective for all learners it is best to use multiple teaching approaches.
Instructional methods and strategies may include:
- lecture
- demonstration
- Visual aids (charts and graphs)
- guided group discussion
- problem solving scenarios
- worksheets
- case study
- experiments
Activities
The final step in course design is to create activities that support the instructional methods and prepare the learner for the assessments. Learning activities should relate directly to learning objectives and course goals.
Activities are the experiences that learners engage in that prepare them to achieve the intended learning objectives. Activities allow the learner to practice applying skills and knowledge. Successful practice should lead to positive results with the assessments.
Using engaging activities provides the learner with the opportunity to practice the skills and apply their knowledge to develop mastery of the course content.
All activities should involve an element of feedback to help the learner apply the information correctly and be successful with the assessments afterwards.
Related Links
Learning goals, objectives, and outcomes
Competencies and Learning Objectives
Learning Goals and Learning Objectives
Components Learning Objectives