Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective to conceive of something new or original.
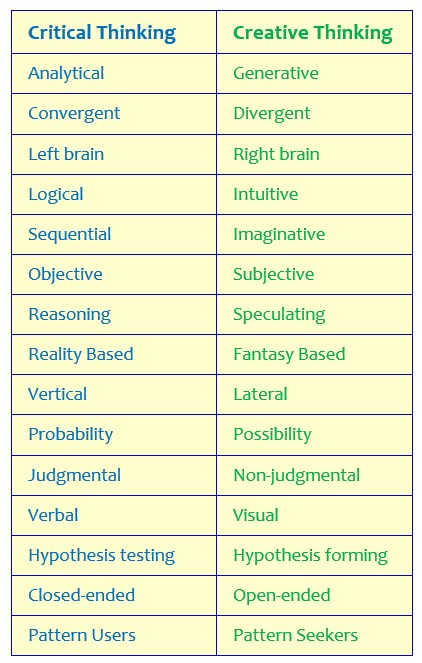
Critical thinking is the logical, sequential disciplined process of rationalizing, analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking – Key Differences
- Creative thinking tries to create something new, while critical thinking seeks to assess worth or validity of something that already exists.
- Creative thinking is generative, while critical thinking is analytical.
- Creative thinking is divergent, while critical thinking is convergent.
- Creative thinking is focused on possibilities, while critical thinking is focused on probability.
- Creative thinking is accomplished by disregarding accepted principles, while critical thinking is accomplished by applying accepted principles.
About Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a process utilized to generate lists of new, varied and unique ideas or possibilities. Creative thinking brings a fresh perspective and sometimes unconventional solution to solve a problem or address a challenge. When you are thinking creatively, you are focused on exploring ideas, generating possibilities, and/or developing various theories.
Creative thinking can be performed both by an unstructured process such as brainstorming, or by a structured process such as lateral thinking.
Brainstorming is the process for generating unique ideas and solutions through spontaneous and freewheeling group discussion. Participants are encouraged to think aloud and suggest as many ideas as they can, no matter how outlandish it may seem.
Lateral thinking uses a systematic process that leads to logical conclusions. However, it involves changing a standard thinking sequence and arriving at a solution from completely different angles.
No matter what process you chose, the ultimate goal is to generate ideas that are unique, useful and worthy of further elaboration. Often times, critical thinking is performed after creative thinking has generated various possibilities. Critical thinking is used to vet those ideas to determine if they are practical.
Creative Thinking Skills
- Open-mindedness
- Flexibility
- Imagination
- Adaptability
- Risk-taking
- Originality
- Elaboration
- Brainstorming
- Imagery
About Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the process of actively analyzing, interpreting, synthesizing, evaluating information gathered from observation, experience, or communication. It is thinking in a clear, logical, reasoned, and reflective manner to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
Critical thinking involves the ability to:
- question
- use logic
- remain objective
- examine
- analyze
- interpret
- evaluate
- reason
- reflect
In general, critical thinking is used to make logical well-formed decisions after analyzing and evaluating information and/or an array of ideas.
On a daily basis, it can be used for a variety of reasons including:
- to form an argument
- to articulate and justify a position or point of view
- to reduce possibilities to convergent toward a single answer
- to vet creative ideas to determine if they are practical
- to judge an assumption
- to solve a problem
- to reach a conclusion
Critical Thinking Skills
- Interpreting
- Analyzing
- Connecting
- Integrating
- Evaluating
- Inferring
- Comparing
- Contrasting
- Classifying
- Sequencing
- Patterning
- Reasoning
- Forecasting
- Hypothesizing
- Critiquing