Verbs for Learning Objectives / Learning Outcomes
The verbs used in learning objectives or learning outcomes should correspond to the level of thought at which the learners are expected to perform or function. The following lists of verbs are provided to help recognize the levels of thought and to help you write learning objectives that address the various levels of skill your learner should attain. By creating learning objectives using these verbs, you indicate explicitly what the learner must do in order to demonstrate learning.
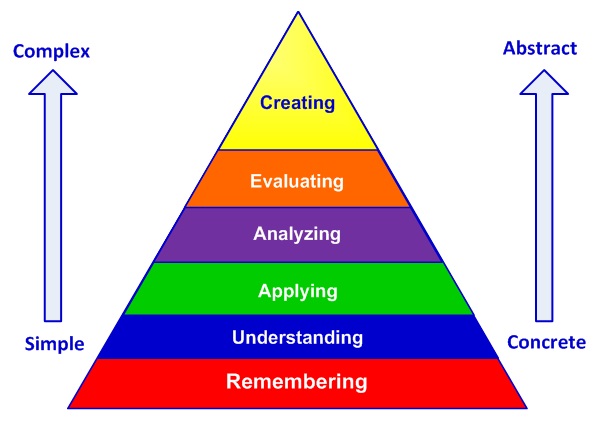
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning
This list is arranged according to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning. Bloom’s Taxonomy classifies thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. The categories are ordered from simple to complex and from concrete to abstract. Each level becomes more challenging as you move higher.
Cognitive competency or complexity begins at the knowledge level learning and advances up the taxonomy to comprehension, application, and then to the higher order thinking skills involved in analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
Determining Verbs for Learning Objectives
When determining your learning objectives, consider using a verb from the appropriate cognitive domain below. This list will help you express specific performance expectations you have of the learners at the completion of the course.
Knowledge
This is the lowest level of learning. This cognitive level focuses on the ability to remember or retrieve previously learned material. The learning standards at this level simply ask the learner to recognize and recall data or information.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Knowledge domain are:
| Arrange
Define Delineate Describe Distinguish Identify Indicate Group List |
Label
Locate Match Memorize Name Outline Order Recall |
Recite
Repeat Record Recognize Specify Select State Underline Write |
Comprehension
This cognitive level focuses on the ability to grasp or construct meaning from material. The learning standards at this level ask the learner to demonstrate understanding of the meaning and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, summarizing, or paraphrasing.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Comprehension domain are:
| Calculate
Conclude Convert Choose Characterize Classify Complete Discuss Describe Depict Determine |
Differentiate
Draw Explain Express Establish Illustrate Interpret Identify Infer Locate Outline |
Paraphrase
Represent Report Review Recognize Restate Summarize Select Sort Tell Translate |
Application
This level focuses on the ability to use information in new ways or situations. The learning standards at this level ask the learner to use the newly acquired information in a new situation or different way from the original context.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Application domain are:
| Apply
Calculate Change Collect Compute Conduct Construct Demonstrate Develop Dramatize Draw Employ Exhibit |
Experiment
Generalize Illustrate Implement Interpret Initiate Make Manipulate Operate Organize Perform Practice Prescribe |
Prepare
Produce Relate Restructure Schedule Shop Solve Show Sketch Teach Translate Use Utilize |
Analysis
This level consider to be a higher order of thinking. This level focuses on the ability to examine and break information or concepts into component parts so that its organizational structure may be understood. The learning standards at this level ask the learner to separate the whole into its parts, in order to better understand the organization of the whole and the relationships between the parts.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Analysis domain are:
| Analyze
Appraise Arrange Calculate Categorize Classify Compare Conclude Contrast Correlate Critique Deduce Debate Detect Determine Develop |
Diagram
Diagnose Differentiate Discover Dissect Distinguish Draw Estimate Evaluate Examine Experiment Explore Group Identify Infer Inquire |
Inspect
Inventory Investigate Order Organize Predict Question Probe Relate Research Scrutinize Separate Sequence Solve Survey Test |
Synthesis
This level also considered to be a higher order of thinking. This level focuses on the ability to compile information in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions. The learning standards at this level ask the learner to put parts together to form a unique new whole or build a structure from diverse elements.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Synthesis domain are:
| Arrange
Appraise Assess Assemble Collect Combine Compile Compose Construct Create Consolidate Choose Compare Critique Derive Design Develop Devise |
Estimate
Evaluate Formulate Forecast Generalize Generate Hypothesize Improve Infer Invent Judge Manage Measure Merge Modify Organize Originate Imagine |
Plan
Predict Prepare Pretend Produce Propose Rate Reorganize Revise Show Select Set up Synthesize Validate Value Test Theorize Write |
Evaluation
This is considered by Bloom to be the highest level of learning. This cognitive level focuses on the ability to make judgments about the value of ideas or materials and able to present and defend opinions based on a set of criteria. The learning standards at this highest level ask the learner to judge, check, critique the value of material to make decisions.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Evaluation domain are:
| Appraise
Argue Arrange Assemble Assess Choose Collect Compose Construct Create Compare Conclude Critique Criticize Debate Decide Deduce Defend Determine Discriminate |
Design
Develop Devise Envision Estimate Evaluate Examine Formulate Grade Inspect Infer Judge Justify Manage Measure Modify Organize Plan Predict Prioritize |
Probe
Prepare Produce Propose Rank Rate Review Reconstruct Recommend Referee Reject Revise Score Select Support Set-up Synthesize Systematize Validate Value |