Instructor-Centered versus Learner-Centered
Traditional Instructor-centered Learning
In a traditional instructor-centered approach to learning, instructors are information providers, and learners are passive recipients of information. The instructor talks and the participants listen.
In this approach, participants are viewed simply as empty vessels who passively receive knowledge from their instructors. The instructor is the center of knowledge and in charge of learning. Participants put all of their focus on the instructor.
This type of learning environment does not allow participants to express themselves, ask questions, and embrace the content. Learners tend to be more competitive and individualistic because they have less opportunity to discuss the information or interact. During activities, the participants work alone, and collaboration is discouraged. If questions are raised by participants, they are answered directly by the instructor without any learner’s involvement.
Learner-centered Learning
A learner-centered approach is about shifting the focus of instruction from the instructor to the learner. This shift offers the best experience for the learner because it has them engage with the instructor, the content, and other learners.
Rather than designing the course from the instructor’s perspective, learner-centered is designed from the learner’s perspective. This approach puts participant’s interests first, acknowledging their needs as central to the learning experience. The learner is not simply a passive participant who receives the information, but rather an active participant in the learning process. They take ownership of the content, determine how it will be useful or relevant to them, and build the cognitive connections to allow the learning to be retained. This is intended to help develop a meaningful connection between the learner and the material being presented.
This approach provides more opportunities for the learner to engage with the content allowing them to build more connections to improve knowledge transfer.
Instructor-Centered versus Learner-Centered
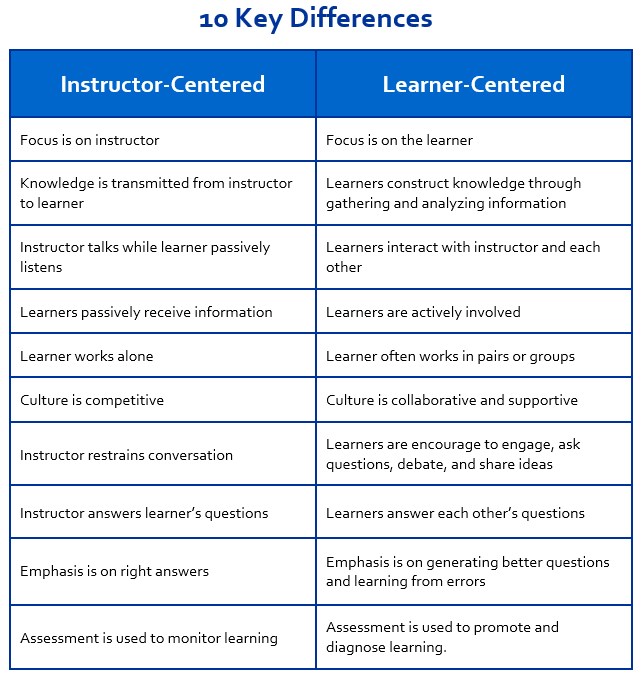
The key differences between the instructor-centered approached versus learner-centered approach:
|
Instructor-Centered |
Learner-Centered |
|
Focus is on instructor |
Focus is on the learner |
|
Instructor is the sole leader |
Leadership is shared |
|
Instructor talks while learner passively listens |
Learners interact with instructor and each other |
|
Learners passively receive information |
Learners are actively involved |
|
Learner works alone |
Learner often works in pairs or groups |
|
Knowledge is transmitted from instructor to learner |
Learners construct knowledge through gathering and analyzing information |
|
The focus is on what the instructor knows about the content |
The focus is on how the learners will use the content |
|
Culture is competitive |
Culture is cooperative, collaborative, and supportive |
|
Instructor restrains conversation |
Learners are encourage to engage, ask questions, debate, and share ideas |
|
Room is quiet with little movement |
Room is active and learner is periodically moving |
|
Instructor makes the rules |
Rules are developed by the instructor and participants in the form of social agreements |
|
Assessment is used to monitor learning |
Assessment is used to promote and diagnose learning |
|
Emphasis is on right answers |
Emphasis is on generating better questions and learning from errors |
|
Instructor answers learner’s questions |
Learners answer each other’s questions |
|
Rewards are mostly extrinsic |
Rewards are mostly intrinsic |
|
Instructor chooses topics |
Learner is included in determining topics |
Links
Teaching Strategies for Adult Learners
