Behavioral Learning
Behaviorism
Behaviorism is the school of thought that seeks to measure only observable behaviors as opposed to internal events like thinking and emotion. Hence, it only examines outward behavior when trying to understand if learning occurred.
Behaviorists define learning as simply the acquisition of new behavior based on environmental conditions. They believe learning actually occurs when new behaviors or changes in behaviors are acquired through associations between stimuli and responses. Thus, association leads to a change in behavior.
Types of Behavioral Learning
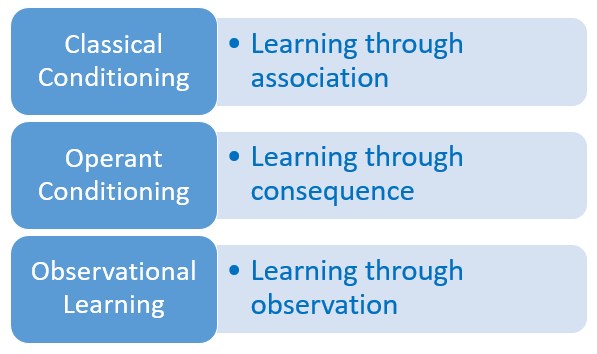
There are three types of behavioral learning:
- Classical Conditioning
- Operant Conditioning
- Observational Learning
About the Three Types of Behavioral Learning
Both classical and operant conditioning are forms of associative learning; meaning associations are made between events that occur together. Observational learning is learning by observing others. Although rooted in behaviorism, the observational learning theory is considered to be a bridge between behaviorism and cognitive learning theories.
Classical Conditioning – Learning through association
Operant Conditioning – Learning through consequences
Observational Learning – Learning through observation
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is a learning process in which an association is made between two stimuli. It occurs when a natural reflex responds to a stimulus. With classical conditioning, two stimuli are linked together to produce a new learned response. One stimulus is a neutral and the other evokes a natural response. After learning the association, the neutral stimulus elicits the conditioned response.
Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning is a learning process in which responses are controlled by their consequences. It is basically a simple feedback system. The likelihood of a certain response occurring is either increased or decreased due to either a reinforcement or a punishment consequence. A reinforcement helps to increase a behavior, while a punishment helps to decrease a behavior.
Observational Learning
Observational learning or modeling is a process in which learning occurs through observing the behaviors of others and then imitating those behaviors. Observational learning allows for learning without any direct change to behavior. This is why it is not considered strict behaviorism.
Links