Brain and Learning
The brain is made up of 100 billion neurons (nerve cells). These neurons connect to thousands of other neurons forming a giant network. Learning takes place and new neural networks are formed when a new connection is made between these neurons.
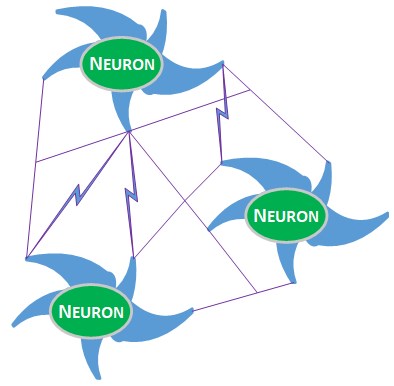
The Brain and Neural Networks
Neurons do not actually touch. However, they do communicate with each other through connections known as synaptic connections. These synapse connections are created through the transmission of electrical and chemical signals sent from one neuron to another. Signals are sent out when the neuron reacts to a stimulus. The neuron fires these signals across a synapse (space between neurons) to another neuron, which receives it through its dendrites. When the message is received a connection is made. This begins the building process of neural networks.
A new neural network is formed every time we learn something new. Thus, neurons connect to thousands of other neurons and networks using trillions of synaptic connections forming one giant network. This network is responsible for everything a person thinks, feels, and remembers.
The Learning Process
The learning process begins when the senses receive stimuli. The brain then reacts to the stimuli by firing neurons. When a neuron fires it transmits chemical signals known as neurotransmitters. Those neurotransmitters are sent across the synapse to relay a message to the dendrites in the receiving neuron. When the message is received a connection is made, and a new memory is formed. The more memories that are formed the bigger and stronger the network becomes.
About Synapses
A synapse is a small gap or junction between two neurons for transmitting information from one neuron to another. The synapses allows a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. The synapses are where much of the activity takes place in the brain.
Synapses are able to control the strength of the signals transmitted between neurons. Synaptic strength varies according to the number of stimuli received during a learning process. These synapses can weaken or strengthen over time.
About Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that relay signals between neurons. These neurotransmitters allow the nerve impulses or signals to travel across the synapse.
Common Neurotransmitters
Dopamine: affects motor movement, mood, behavior, attention, learning, reinforcement, and pleasure
Serotonin: affects emotion, mood, sleep, appetite, impulsivity, aggression
Acetylcholine: affects movement, learning, memory, REM sleep, and plays a role in attention and arousal
Glutamate: involved in learning and emotion
Endorphins: Provide relief from pain and feelings of pleasure and well-being