The Human Brain
The human brain is the center of the nervous system. It collects information, acts on that information and stores the result for future reference. The brain is hugely interconnected but three major components can be identified: the cerebrum, the cerebellum and the brain stem.
Three major components:
- the cerebrum
- the cerebellum
- the brain stem
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located at the lower back. The cerebellum helps with muscle coordination and balance. The cerebellum plays an instrumental role in balance, motor control, but is also involved in some cognitive functions such as attention, language, emotional functions and in the processing of procedural memories.
Brainstem
The brainstem consists of the medulla, the pons and the midbrain. The brain stem is located at the lower extension of the brain where it connects to the spinal cord. While the upper brain gives your life quality (movement, reasoning, speech), the brainstem keeps you alive. Everything necessary for survival such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure is controlled by the brain stem.
The cerebrum or the cerebral cortex
The cerebrum or the cerebral cortex consists of the cortex, large fiber tracts (corpus callosum) and some deeper structures (basal ganglia, amygdala and hippocampus). The cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language and consciousness.
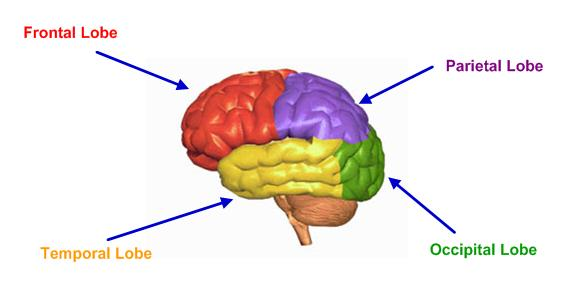
Four Lobes of the Human Brain
Cerebrum or the cerebral cortex can further be divided into four lobes:
- The frontal lobe
- The parietal lobe
- The temporal lobe
- The occipital lobe
Cerebrum or the cerebral cortex can further be divided into four lobes:
The frontal lobe (thinking, conceptualization, planning) – it involves conscious thought and higher mental functions including planning, organizing, problem solving, selective attention, personality, behavior and emotions.
The parietal lobe (movement, orientation, calculation, recognition) is involved in controlling sensation (touch, pressure), and in the manipulation of objects in determining spatial sense and navigation by controlling fine sensation (judgment of texture, weight, size, shape).
The temporal lobe (sound and speech processing, aspects of memory) it involves with the senses of smell and sound, the processing speech and vision, verbal memory (memory of words and names) and visual memory (memory for pictures and faces).
The occipital lobe – is mainly for visual processing. It is for visual reception and association, including recognition of shapes and colors.
Brain Theories
Roger Sperry initiated the study of the relationship between the brain’s right and left hemispheres. His significant research clearly demonstrated that the brain is divided into two major parts or hemispheres, the right brain and the left brain.
Research into the brain’s function and individuals’ brain dominance was further enhanced by Ned Hermann. Herrmann drew on the work of Sperry and developed the theory of brain dominance where people develop a dominant mode of thinking preference. These can range from an analytical “left brain” approach to “right brain” approaches involving pattern matching and intuitive understanding.
Herrmann then went onto develop the four-quadrant model of cognitive preferences and a questionnaire called the Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI). The inspiration for this model came from dividing the human brain into as four different systems with four preferred styles:
A: Left cerebral hemisphere – analytical
B: Left limbic system – sequential
C: Right limbic system – interpersonal
D: Right cerebral hemisphere – imaginative
Left Brain vs. Right Brain Theory
Roger Sperry initiated the study of the relationship between the brain’s right and left hemispheres. His significant research clearly demonstrated that the brain is divided into two major parts or hemispheres, the right brain and the left brain. His research also identified that each of the parts of the brain specializes in its own style of thinking, processes information differently, and has different capabilities. Sperry found that the left half of the human brain tends to function by processing information in an analytical, rational, logical, sequential way. The right half of the brain tends to function by recognizing relationships, integrating and synthesizing information, and arriving at intuitive insights.
Additionally, he found that people prefer one type of thinking over the other. For example, a person who is “left-brained” is often said to be more logical, analytical and objective, while a “right-brained” person is said to be more intuitive, creative, and subjective.
The Left Brain
The left brain is associated with verbal, logical, and analytical thinking. It excels in naming and categorizing things, symbolic abstraction, speech, reading, writing, arithmetic. The left brain is very linear as it places things in sequential order.
The left-brain is often described as being better at:
- Language
- Logic
- Critical thinking
- Numbers
- Reasoning
The Right Brain
The right brain functions in a non-verbal manner and excels in visual, spatial, perceptual, and intuitive information. The right brain’s style of processing is nonlinear and non-sequential. The right brain looks at the whole picture and quickly seeks to determine the spatial relationships of all the parts as they relate to the whole. The right brain is often associated with the realm of creativity.
Some of the abilities associated with the right side of the brain include:
- Recognizing faces
- Expressing emotions
- Reading emotions
- Color
- Visual Images
- Music
- Intuition
- Creativity
Brain Dominance Theory
According to the theory of left-brain or right-brain dominance, each side of the brain controls different types of thinking. We tend to process information using our dominant side. However, the learning process is enhanced when all of our senses are used including our less dominate hemisphere.
Brain Dominance Test
http://www.web-us.com/brain/braindominance.htm