Honey Mumford Model
Honey and Mumford’s Learning Stages and Styles
The Honey Mumford Model is based on the Kolb learning styles, but with a few differences. It is basically the same as Kolb’s model, with just a few differences.
First, Peter Honey and Alan Mumford adapted David Kolb’s model to use in business.
Therefore, the stages in the cycle were renamed to accord with managerial experiences as they deal with problems and decision-making.
Learning Cycle
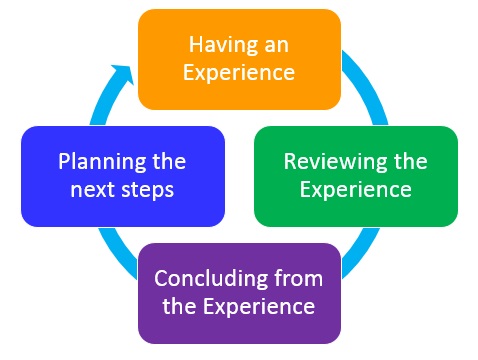
The typical depiction of these stages and styles would be respectively clockwise from 12 on a four-stage cyclical flow diagram.
The Honey & Mumford stages are:
Stage 1: having an experience
Stage 2: reviewing the experience
Stage 3: concluding from the experience
Stage 4: planning the next steps
Stage 1 – Having an Experience: this is the “here and now” stage. This involves seeking challenges and immediate experience, and being open-minded.
Stage 2 – Reviewing the Experience: this is the “stand back” stage. This involves gathering data, pondering, and analyzing.
Stage 3 – Concluding from the Experience: This is the “thinking things through” stage. This involves thinking in logical steps, assimilating facts into coherent theories, and being rationally objective.
Stage 4 – Planning the next steps: This is the “trying out new ideas” stage. This stage involves trying out new ideas, problem solving, and decision-making.
Four Resultant learning-styles
The four resultant learning-style types from the model are Activists, Reflectors, Theorists, and Pragmatists.
| Style | Preference
|
| Activists | want to learn by diving straight in to new experiences, and do not particularly like theory
|
| Reflectors | like to stand back and gather information before coming to a conclusion
|
| Theorists | want to fully understand the theory behind a subject before they feel comfortable with it
|
| Pragmatists | want to see the practical use of what they’re learning, and want practical techniques
|
Additional Learning Styles
Felder-Silverman Learning Style
Herrmann’s Brain Dominance HBDI
Left-brain and Right-brain Preferences
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator MBTI