The Index of Learning Styles
Felder & Soloman – The Index of Learning Styles
People take in and process information in different ways based on their individual preferences. It is helpful to determine your own specific style or preference. There are various assessments that can help determine your style. “The Index of Learning Styles” (ILS) is one of the most popular assessments.
“The Index of Learning Styles” was developed by Richard Felder and Barbara Soloman of North Carolina State University. The “Index of Learning Styles” is an on-line tool used to assess preferences on four dimensions of a learning style model.
The Index of Learning Styles Questionnaire contains 44 two choice questions. The questionnaire is available on-line.
http://www.engr.ncsu.edu/learningstyles/ilsweb.html
The questionnaire results create a profile that indicate a learner’s preferences. A person’s learning style profile provides an indication of probable strengths and possible tendencies that might lead to challenges in learning.
The Learning Style Model
“The Index of Learning Styles” questionnaire is based on a learning styles model developed by Dr. Felder and Dr. Linda Silverman. According to their model there are four dimensions of learning styles. Each of the four scales of the index of learning styles has two opposite preferences. You can think of these dimensions as a continuum with one learning preference on the far left and the other on the far right.
The four dimensions
Everyone typically uses all preferences at different times, but they usually prefer one over the other.
The Four Dimensions
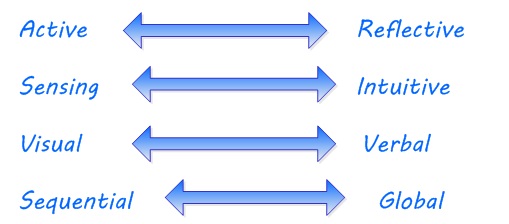
The active/reflective continuum: how do you prefer to process information?
| Active | Reflective |
| Active learners learn by doing something with information. They prefer to process information by talking about it and trying it out. They like discussing, applying, or explaining it to others. | Reflective learners learn by thinking about information. They prefer to think things through and understand things before acting. |
The sensing/intuitive continuum: how do you prefer to take in information?
| Sensing | Intuitive |
| Sensing learners prefer to take in information that is concrete and factual. They are oriented towards details, facts, and figures and prefer to use proven procedures. They are realistic and like practical applications. Sensors like solving problems by established methods and dislike complications and surprises. | Intuitive learners prefer to take in information that is abstract, original, and oriented towards theory. They prefer discovering possibilities and relationships. They look at the big picture and try to grasp overall patterns. They like innovation and dislike repetition. |
The visual/verbal continuum: how do you prefer information to be presented?
| Visual | Verbal |
| Visual learners prefer visual presentations of material. They like pictures, diagrams, graphs, charts, time lines, films, and demonstrations. | Verbal learners prefer explanations with words – written and spoken explanations. |
The sequential/global continuum: how do you prefer to organize information?
| Sequential | Global |
| Sequential learners prefer to organize information in a linear, orderly fashion.
They tend to gain understanding in linear steps, with each step following logically from the previous one. They prefer to work with information in an organized and systematic way. |
Global learners prefer to organize information more holistically and in a seemingly random manner without seeing connections. They often are able to solve complex problems quickly, but they may have difficulty explaining how they did it. |
Additional Learning Styles
Felder-Silverman Learning Style
Herrmann’s Brain Dominance HBDI
Left-brain and Right-brain Preferences
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator MBTI