Felder-Silverman Learning Style Model
People take in and process information in different ways based on their individual preferences. Richard Felder and Linda Silverman developed a model to depict different learning styles and preferences.
Felder and Silverman developed their learning style model for two reasons:
- to capture the learning style differences among engineering students, and
- to provide a good foundation for engineering instructors to design a teaching approach that would address the learning needs of all students.
Although the study was focused on engineering students, the model can be helpful to understand the various learning styles.
The Felder-Silverman Model denotes four areas of personality that contribute to learning. The model creates four dimensions of learning styles. These dimensions can be viewed as a continuum with one learning preference on the far left and the other on the far right. They are active or reflective, sensing or intuitive, visual or verbal, inductive-deductive, and sequential or global. A combination of these styles makes up the individuals learning preferences.
NOTE: The original model had another dimension; the inductive/deductive dimension. This dimension was later dropped in 2002 by Dr. Felder.
The Four Dimensions
This model classifies individuals along the following dimensions:
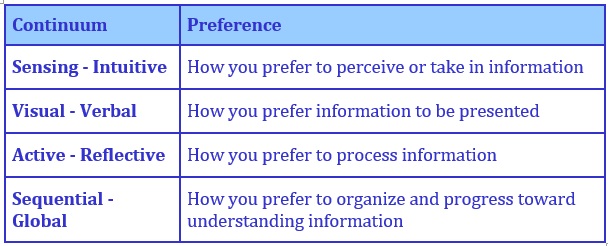
Sensing-Intuitive continuum determines how you prefer to perceive or take in information.
Visual-Verbal continuum determines how you prefer information to be presented.
Active-Reflective continuum determines how you prefer to process information.
Sequential-Global continuum determines how you prefer to organize and progress toward understanding information.
Felder- Silverman Learning Preferences
| Type of Learner | Preferences |
| sensing | Prefers concrete thinking, practical, concerned with facts and procedures |
| intuitive | Prefers conceptual thinking, innovative, concerned with theories and meanings |
| visual | prefers visual representations, pictures, diagrams, and flow charts |
| verbal | prefers written and spoken explanations |
| active | Prefers to try things out, working with others in groups |
| reflective | Prefers thinking things through, working alone or with familiar partner |
| sequential | Prefers linear thinking, orderly, learns in small incremental steps |
| global | Prefers holistic thinking, systems thinkers, learns in large leaps |
Additional Learning Styles
Felder-Silverman Learning Style
Herrmann’s Brain Dominance HBDI
Left-brain and Right-brain Preferences
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator MBTI