Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is the process of keenly analyzing and evaluating information to draw conclusions in order to generate ideas on possible solutions to problems. This deep level of thinking involves synthesizing, conceptualizing, and applying relevant information that has been analyzed to make reasoned judgments. It requires the highest levels of thinking. The lower levels of thinking include remembering, understanding, and applying information. The higher levels of thinking include analyzing information, evaluating alternatives, and creating or generating ideas based on the analysis.
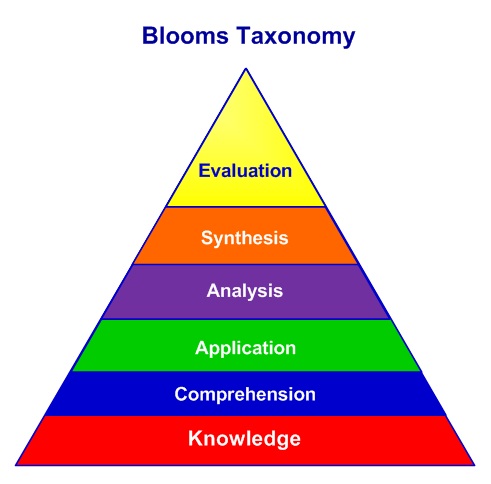
Bloom’s Taxonomy – Levels of Thinking
| Knowledge | Remembering, recalling or retrieving previously learned information |
| Comprehension | Understanding or grasping the meaning from material. Able to state a problem or concept in one’s own words. |
| Application | Using learned information, or implementing material or concept in a new situation. |
| Analysis | Separating or breaking down material or concepts into component parts so that its organizational structure may be better understood. Able to distinguish between facts and inferences. |
| Synthesis | Building a structure or pattern from diverse elements, or putting parts together to form a coherent new whole. |
| Evaluation | Making judgments about the value of ideas or materials for a given purpose. |
Steps in Critical Thinking
The steps in critical thinking involve; defining a problem, gathering information, analyzing evidence, generating ideas, recognizing and assessing implications and consequences, and identifying a reasoned solution.
In order to be successful, critical thinkers also need to;
- remain open minded
- avoid emotional reasoning
- avoid oversimplification
Steps in Critical Thinking
Critical thinkers should deal with the components of a complex problem in an orderly manner:
- Identify issues or problems
- Define the problem with a clear and concise statement of the problem
- Gather relevant information
- Assess the credibility and accuracy of information and supporting evidence
- Analyze information
- Search for reasons and root causes of problem
- Draw conclusions and generate theories
- Formulate questions to test conclusions and theories
- Identifying potential options or solutions to resolve issue or problem
- Assess implications and consequences of possible options / solutions
- Select the best solution
- Implement and test the solution
People who develop critical thinking skills are better able to think analytically, independently, and globally to find solutions to problems.
Our Development Series provides information of skill building, tools used to analyze information, and techniques to generate ideas.
Links