Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities
Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (KSAs) are categories of qualifications and personal attributes that an individual needs in order to effectively perform the duties of a specific job. Usually, the hiring organization will create a list of KSAs as a guideline to help identify the ideal candidates for a position.
KSAs Defined
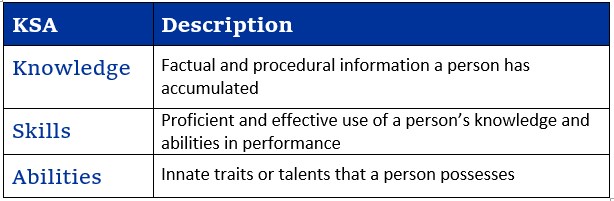
Knowledge: factual and procedural information a person has accumulated
Skills: proficient and effective use of a person’s knowledge and abilities in performance
Abilities: innate traits or talents that a person possesses
About Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities
Knowledge
Knowledge refers to the factual and procedural information a person acquired through education or experience. It can be obtained from reading reference material, attending a training class, or direct experience.
Knowledge is the theoretical or practical understanding of a concept or subject. It can be measured with written or oral exams where a person documents or explains what they know about the topic.
A person can gain additional knowledge or understanding by applying what they know and learning from that experience. However, having knowledge of how to do something does not necessarily mean that a person can do it. A person may have an understanding of a topic and all the steps involved in the process, but have no experience applying it.
Examples of knowledge:
- workplace safety regulations
- steps involved in a process
- what to do in an emergency
Skills
Skills refer to the proficient and effective use a person’s knowledge and abilities in performance that can be measured in time and precision. They are the capabilities or proficiencies a person acquires through deliberate, systematic, and sustained effort in order to effectively carryout activities or job functions involving ideas, things, and/or people. It can be further developed through training and/or hands-on experience.
Skills can be measured and observed. A test can be used to measure quantity and quality of performance.
Examples of skills:
- typing
- operating a vehicle or machine
- programming software
Abilities
Abilities are the qualities or attributes of being able to perform an observable activity. Abilities tend to be innate traits that a person possesses or acquired without formal instructions. These include areas such as talent and emotional intelligence.
Abilities are much harder to teach, test, or measure then skills or knowledge.
Examples:
- planning and organizing
- show empathy
- thinking fast
Difference between Skill and Ability
Abilities are often confused with skills, yet there is a significant difference. Abilities are natural or intrinsic, while skills are learned behaviors.
Additionally, a skill can be taught, tested, and measured. However, abilities are a broad term for human capacity that are harder to teach, test, or measure.
Example:
Skill – operate a vehicle
Abilities – process information quickly and to react to other drivers
Example:
Skill – Cut hair
Ability – keep hand steady
Interrelationship of KSAs
Skills are a composite of abilities and knowledge. Basically, ability and knowledge combine to create skills that can be applied.
Ability + Knowledge = Skill
Skills can be developed and improved over time. However, the underlying abilities and knowledge are needed in order for the skills to be further developed.
Example:
Skill – shoot a basketball
Knowledge – shooting techniques
Ability – hand eye coordination and ability to jump
Example:
Skill – make a cake
Knowledge – ingredients and recipe steps
Ability – to measure and mix ingredients
Additional Links
Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes
Knowledge, Skills, Attitudes and Habits
