Cognitive Learning Theory (CLT) is about understanding how the human mind works while people learn. The theory focuses on how information is processed by the brain, and how learning occurs through that internal processing of information. It is based on the idea that people mentally process the information they receive, rather than simply responding to stimuli from their environment.
About the Cognitive Learning Theory
The Cognitive Learning Theory is a broad theory used to explain the mental processes and how they are influenced by both internal and external factors in order to produce learning in an individual. The theory is credited to Educational psychologist Jean Piaget. He believed knowledge is something that is actively constructed by learners based on their existing cognitive structures.
Piaget disagreed with the behaviorist theory which focuses strictly on observable behavior. He concentrated more attention to what went on inside the learner’s head, instead of how they reacted.
Behaviorists Approach vs. Cognitive Approach
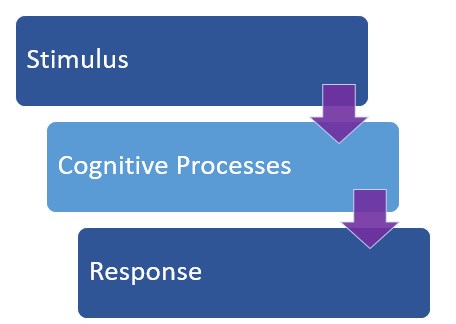
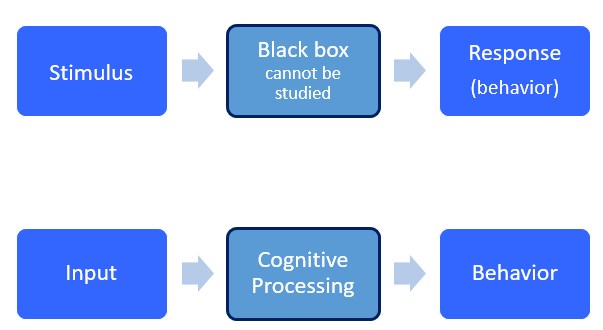
The behaviorists approach only studies external observable behavior that can be objectively measured. This theory is based on a stimulus and a person’s response to that stimulus. Behaviorists believe that internal behavior cannot be studied because internal mental processes cannot be observed and objectively measured. In other words, we cannot see what happens in a person’s mind, so therefore, we cannot measure it.
However, unlike behaviorism, the cognitive approach believes that internal mental processes can be scientifically studied. It focuses on the thought process behind the behavior. Cognitive psychologists believe in order to understand behavior, you have to understand what goes on in the brain to cause the behavior. Therefore, the cognitive approach to learning pays more attention to what goes on inside the learner’s head and focuses on mental processes, rather than just observable behavior. Changes in behavior are observed, but only as an indicator to what is going on in the learner’s brain.
The Cognitive Learning Process
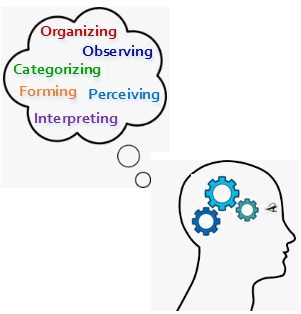
Cognitive learning is centered on the mental processes by which the learner takes in, interprets, stores, and retrieves information. These mental processes occur between stimulus/input and response/output. The individual takes in the stimulus, processes it in their mind, and then acts upon the stimulus. Those mental processes have several elements including;
- attention
- observing
- perception
- interpreting
- organizing
- memory (storing and retrieval)
- categorizing
- forming generalizations
It is believed that individuals act on beliefs, thoughts, knowledge, attitudes, feelings, as well as understanding about themselves and the environment when interpreting stimulus.
Links