Thinking Skills
Thinking skills are the mental activities you use to process information, make connections, make decisions, and create new ideas. You use your thinking skills when you try to make sense of experiences, solve problems, make decisions, ask questions, make plans, or organize information.
Everybody has thinking skills, but not everyone uses them effectively. Effective thinking skills are developed over a period of time. Good thinkers see possibilities where others see only obstacles or roadblocks. Good thinkers are able to make connection between various factors and be able to tie them together. They are also able to develop new and unique solutions to problems.
Thinking refers to the process of creating a logical series of connective facets between items of information. Often times, thinking just happens automatically. However, there are times when you consciously think. It may be about how to solve a problem or making a decision. Thinking enables you to connect and integrate new experiences into your existing understanding and perception of how things are.
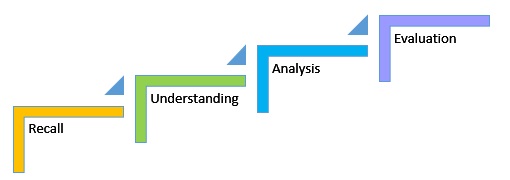
The simplest thinking skills are learning facts and recall, while higher order skills include analysis, synthesis, problem solving, and evaluation.
Core Thinking Skills
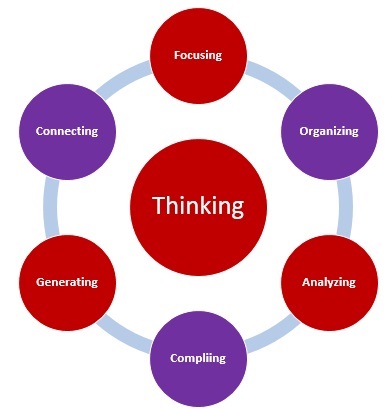
Thinking skills are cognitive operations or processes that are the building blocks of thinking. There are several core thinking skills including focusing, organizing, analyzing, evaluating and generating.
Focusing – attending to selected pieces of information while ignoring other stimuli.
Remembering – storing and then retrieving information.
Gathering – bringing to the conscious mind the relative information needed for cognitive processing.
Organizing – arranging information so it can be used more effectively.
Analyzing – breaking down information by examining parts and relationships so that its organizational structure may be understood.
Connecting – making connections between related items or pieces of information.
Integrating – connecting and combining information to better understand the relationship between the information.
Compiling – putting parts together to form a whole or building a structure or pattern from diverse elements.
Evaluating – assessing the reasonableness and quality of ideas or materials on order to present and defend opinions.
Generating – producing new information, ideas, products, or ways of viewing things.
Classifications and Types of Thinking
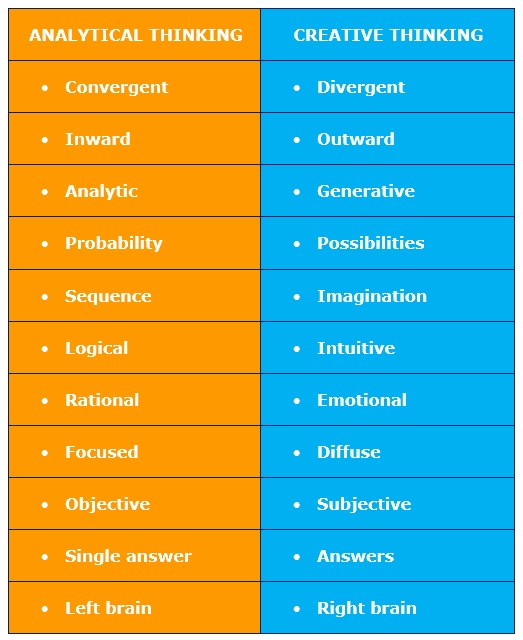
Convergent or Analytical Thinking: Bringing facts and data together from various sources and then applying logic and knowledge to solve problems or to make informed decisions.
Divergent thinking: Breaking a topic apart to explore its various components and then generating new ideas and solutions.
Critical Thinking: Analysis and evaluation of information, beliefs, or knowledge.
Creative Thinking: Generation of new ideas breaking from established thoughts, theories, rules, and procedures.
Metacognition
Thinking about thinking is called Metacognition. It is a higher order thinking that enables understanding, analysis, and control of your cognitive processes. It can involve planning, monitoring, assessing, and evaluating your use of your cognitive skills.
Thinking Skills
In the simplest form, convergent thinking or deductive reasoning looks inward to find a solution, while divergent or creative thinking looks outward for a solution.
Both thinking skills are essential for school and life. Both require critical thinking skills to be effective. Both are used for solving problems, doing projects and achieving objectives. However, much of the thinking in formal education focuses on the convergent analytical thinking skills such as following or making a logical argument, eliminating the incorrect paths and then figuring out the single correct answer.
Standardized tests such as IQ tests only measure convergent thinking. Pattern recognition, logic thought flow, and the ability to solve problems with a single answer can all be tested and graded. Although it is an extremely valuable skill, there are no accurate tests able to measure divergent or creative thinking skills.
Links
Critical Thinking skills
Divergent and Convergent thinking skills are both “critical thinking” skills.
Critical thinking refers to the process of actively analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating and reflecting on information gathered from observation, experience, or communication and is focused on deciding what to believe or do.
Critical thinking is considered a higher order thinking skills, such as analysis, synthesis, and problem solving, inference, and evaluation.
The concept of higher order thinking skills became well known with the publication of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. Bloom’s Taxonomy was primarily created for academic education; however, it is relevant to all types of learning.
Often times when people are problem solving or decision making, he or she flips back and forth between convergent and divergent thinking. When first looking at a problem, people often analyze the facts and circumstances to determine the root cause. After which, they explore new and innovative options through divergent thinking, then switch back to convergent thinking to limit those down to one practical option.
Author: James Kelly, September 2011